Ganoderma Mushrooms: Medicinal Benefits, Cultivation & Global Impact
The Ganoderma genus is one of the most revered groups of fungi in the world. Known for their hard, woody fruiting bodies and powerful medicinal properties, these mushrooms have been used for centuries in traditional medicine. The most famous species, Ganoderma lucidum, commonly referred to as Reishi in Japan or Lingzhi in China, has been a cornerstone of Eastern herbal medicine for millennia. Another noteworthy species is Ganoderma tsugae, or Hemlock Reishi, which grows exclusively on Eastern Hemlock trees (Tsuga canadensis).
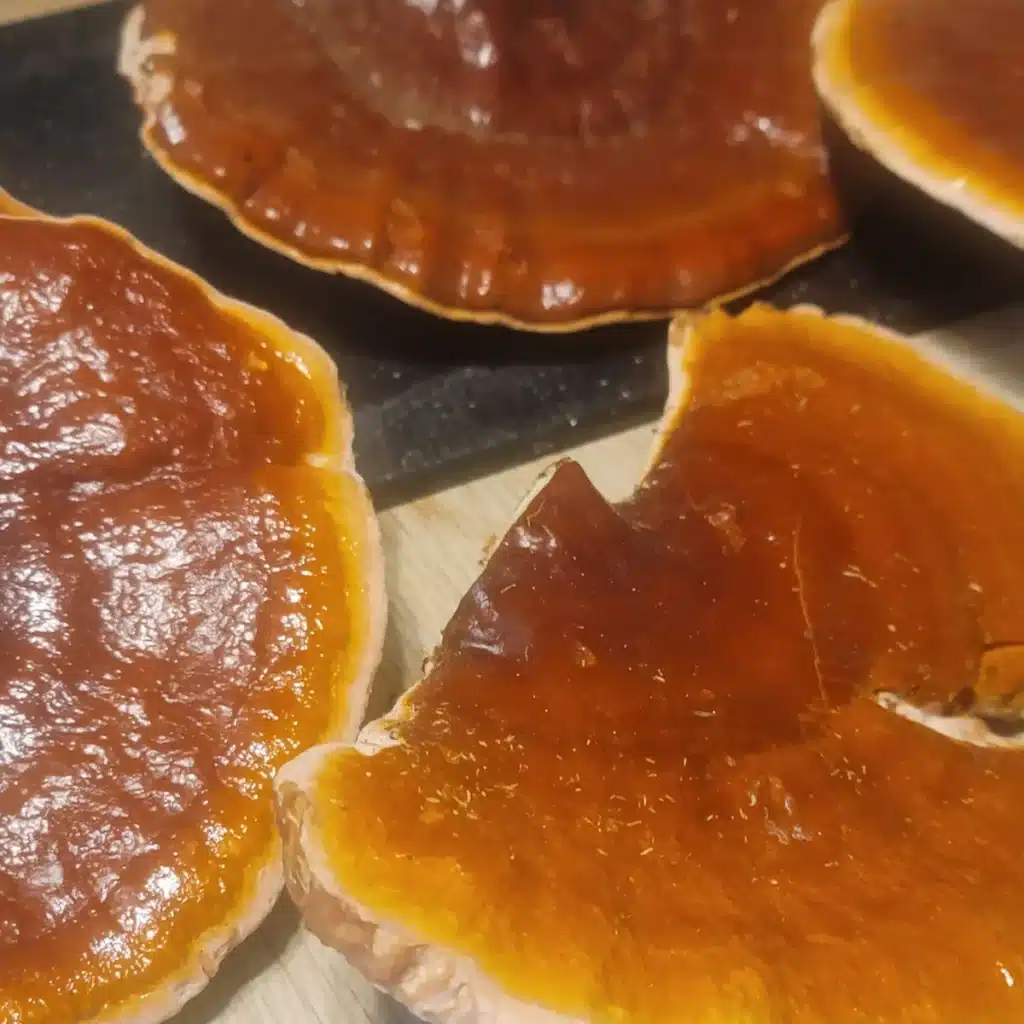

Today, modern science continues to validate the health benefits of Ganoderma mushrooms, and global demand for these fungi is soaring. The United States has become a major player in mushroom cultivation and exports, with innovative growing techniques making Ganoderma more accessible than ever.
The Many Faces of Ganoderma: Key Species
Ganoderma lucidum (Reishi, Lingzhi)
- Found predominantly in Asia, particularly China, Japan, and Korea
- Used in traditional medicine for immune support, stress reduction, and longevity
- Contains high levels of triterpenoids, polysaccharides, and antioxidants
- Often grown commercially on logs or hardwood sawdust blocks
Ganoderma tsugae (Hemlock Reishi)
- Found in North America, particularly in the Eastern United States and Canada
- Thrives on Eastern Hemlock (Tsuga canadensis) trees
- Contains similar medicinal properties to G. lucidum, with a slightly different triterpene profile
- Often sought after by wild foragers due to its preference for old-growth forests
Other Notable Species
- Ganoderma applanatum (Artist’s Conk) – Known for its hard, perennial fruiting body and its use in herbal medicine and wood carving.
- Ganoderma sinense – Used similarly to G. lucidum but contains a different chemical composition.
- Ganoderma resinaceum – Found in Europe and used in traditional remedies.
Medicinal Use: Ancient Wisdom Meets Modern Science
Traditional Uses in Asia
For over 2,000 years, Ganoderma lucidum has been revered in Chinese medicine as a “mushroom of immortality.” It has been used to:
- Boost immune function
- Enhance liver health
- Improve cardiovascular function
- Reduce stress and promote longevity
Ancient texts, such as the Shen Nong Ben Cao Jing, describe Ganoderma as a tonic for “calming the mind” and “strengthening the spirit.” It was reserved for emperors and high-ranking officials, signifying its powerful effects.
Scientific Evidence and Modern Research of Ganoderma Mushrooms
Contemporary studies have validated many of the traditional claims. Research has identified several bioactive compounds, including triterpenoids, polysaccharides, and peptidoglycans, that contribute to Ganoderma‘s medicinal effects. Some notable findings include:
- Immune System Modulation: Ganoderma lucidum stimulates immune response by increasing the activity of natural killer (NK) cells and T cells, which help fight infections and even cancer.
- Anti-Inflammatory Effects: Studies have shown Ganoderma extracts reduce inflammation by regulating cytokine production, making it a promising natural remedy for autoimmune diseases.
- Cardiovascular Benefits: Ganoderma may help lower LDL cholesterol and regulate blood pressure, supporting overall heart health.
- Antitumor Potential: Research suggests that polysaccharides in Ganoderma may inhibit tumor growth and improve the efficacy of conventional cancer treatments.
External Link: Research Study on Ganoderma’s Medicinal Benefits
Global Cultivation and the Role of the USA in Mushroom Exports
While Ganoderma has traditionally been cultivated in China, Japan, and Korea, the United States has emerged as a new leader in mushroom cultivation. With advancements in controlled-environment agriculture, American mushroom farms are producing high-quality Reishi and other medicinal mushrooms at an increasing scale.
Growing Ganoderma requires specific conditions, including:
- A nutrient-rich substrate (e.g., hardwood logs, sawdust, or grain-based mixtures)
- Humidity levels between 80-90%
- Consistent air exchange to prevent contamination
Many cultivators in the U.S. are now using liquid culture techniques to propagate Ganoderma more efficiently. If you’re looking to start your own cultivation, check out our Liquid Culture Selection at Bas Mycology.
The Future of Ganoderma and Medicinal Mushrooms
With ongoing research into their potential applications in cancer treatment, neuroprotection, and metabolic health, Ganoderma mushrooms continue to captivate scientists and herbalists alike. As public awareness grows and consumer demand rises, the future of Ganoderma cultivation and use looks brighter than ever.
Final Thoughts
Ganoderma mushrooms are more than just fascinating fungi—they are powerful allies in both traditional medicine and modern science. With species like G. lucidum and G. tsugae offering a wide range of health benefits, their popularity will only continue to grow. Whether you’re interested in wild foraging, cultivation, or medicinal research, Ganodermaremains a cornerstone of the mushroom kingdom.
If you find yourself interested in learning to grow your own Ganoderma Reishi mushrooms check out our Reishi Liquid culture we offer.